How it Works:
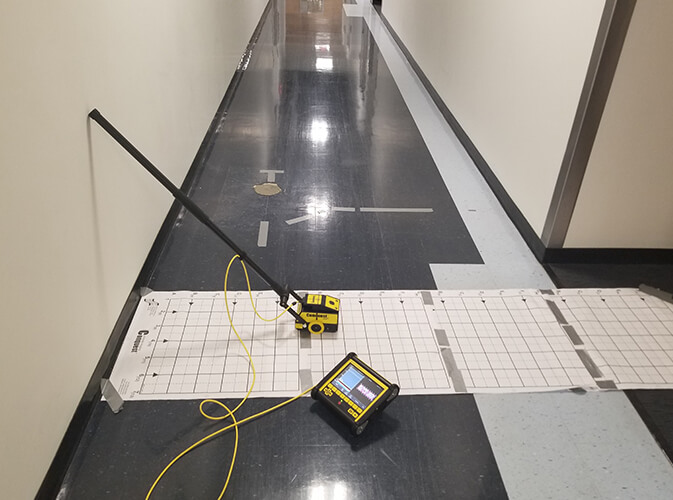
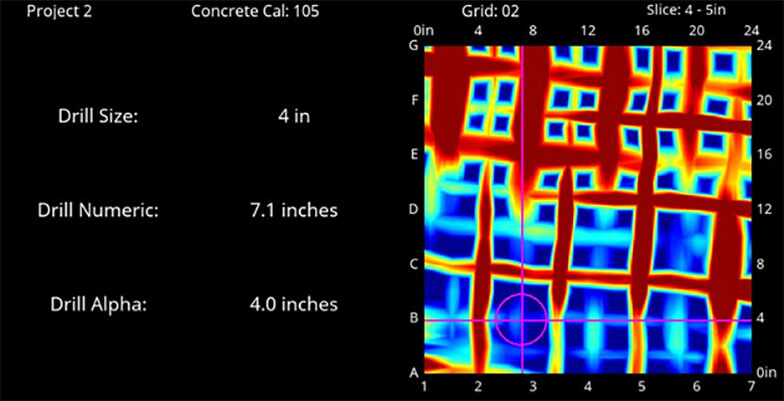
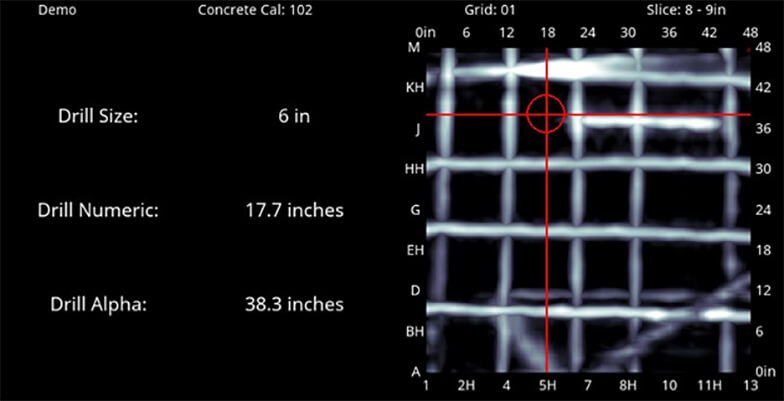
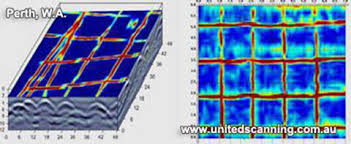
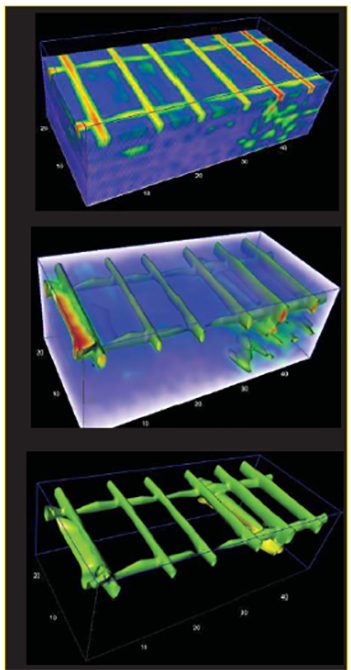
Concrete or Cement Scanning is a type of nondestructive GPR Testing. The process is used to detect and protect utilities and other structural supports in concrete. If you are going to start with the coring and cutting into the concrete, first of all, it is crucial for you to know what is inside. Concrete walls and floors usually contain electric cables, fiber optics, rebar, voids, mesh, conduit, and tension cables. Concrete scanning works like an X-Ray machine to image all these.
Why Use Concrete/Cement Scanning:
Concrete Scanning is a smart technology which assures real time diagnosis of the potential risks and problem areas prior to the drilling or cutting into the concrete structure. Unlike X-Ray, Concrete Scanning is nondestructive as it does not require job site evacuation of a concrete structure. The technology is safer than the X-Ray diagnosis as it is nondestructive and can be performed without disturbing surrounding areas or inhabitants. Along with that, Concrete/Cement Scanning ensures the safety of the workers as well as the area, as it keeps everyone at the job safe. Not only this, but it also reduces the financial damage which can be caused if you accidentally cut a wire or any other object. Not to mention, it also saves you from other hazards and unwanted delays. Therefore, cement scanning is not only a profit-friendly system it also ensures that you get the job done on time.
Why Concrete/Cement Scanning is an Effective Technique:
Damage of concrete structural elements such as rebar, poste tension cables and conduit can be costly and dangerous at the same time. Other than that you may have to deal with further difficulties due to the project delays, which will eventually increase the expense of the project. Therefore, it is better to take the precaution prior coring or cutting into the concrete surfaces to reduce the chances of potential risks. With concrete scanning, you can save your time and money as it allows you to prioritize your tasks as per the need.
What do we Scan with Concrete/Cement Scanning?
EASY
- Rebar
- Post-tension cables
- Metallic and non-metallic conduits
- wire mesh
- Radiant heat tubes
- L dowel bar and e-bars in road/bridge construction
- Hollow-core slab
- Measure cover depth above targets
- Measure asphalt thickness over concrete
MEDIUM
- Glass rebar
- Voids beneath slab-on-grade
- Vertical rebar in columns
- Depth of concrete slab-on-grade.
DIFFICULT
- Corroded rebar
- Cracks in concrete